In-situ polymerization of gel polymer electrolyte using electron beam technology
Young Hwan Lee1, Tae Sung Ha1, Ji Hyun Park1.
1R&D Lab, Seoul Radiology Services, 37-10, Maengdongsandan-ro, Maengdong-myeon, Eumseong-gun, 27733, Korea
Due to the popularization of portable electronic devices and electric vehicles, the demand of high-performance lithium-ion batteries is increasing, but there are still hurdles to overcome for more public use, such as safety problems which is believed to come from the vulnerabilities of liquid electrolyte to harsh environmental conditions. To solve this problem, a gel electrolyte is a very good alternative. The conventional film-type gel electrolyte manufactured in an ex-situ method makes the process complicate, and not suitable for mass production.
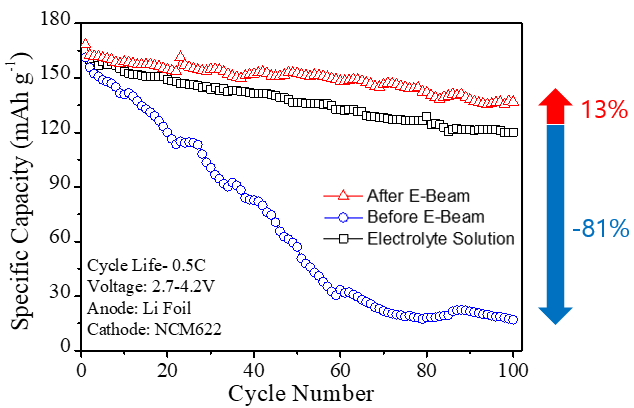
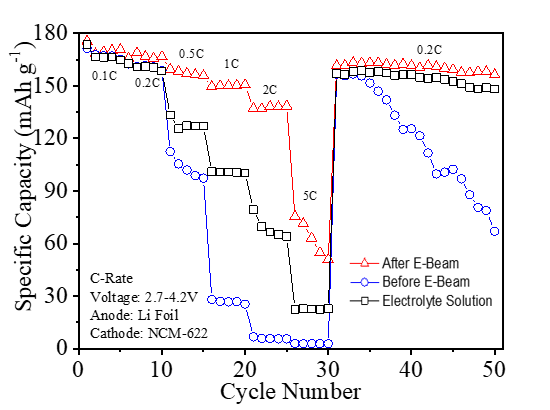
In this work, a series of novel gel polymer electrolytes(GPE) based on poly ethylene glycol(PEG) derivative and acrylate derivative were produced and characterized. To synthesize GPE in an in-situ method, a gel precursor mixed with a PEG derivative, an acrylate derivative, and a liquid electrolyte was injected into the cell and free radical polymerization of monomers performed using 10MeV electron beam irradiation. The characterization of the GPE cell was done by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy(EIS), cyclic voltammetry(CV), discharge and C-rate. EIS showed ionic conductivity of 90% level of liquid electrolyte at room temperature. Capacity retention and reversibility were confirmed from the CV curve. Discharge and C-rate data demonstrate the initial discharge capacity and retention rate.