
Monte Carlo investigation of the equivalency of the electron and photon spectra of e-beam, x-ray, and gamma radiation
Thomas Kroc1.
1IARC, Fermilab, Batavia, IL, United States
Introduction
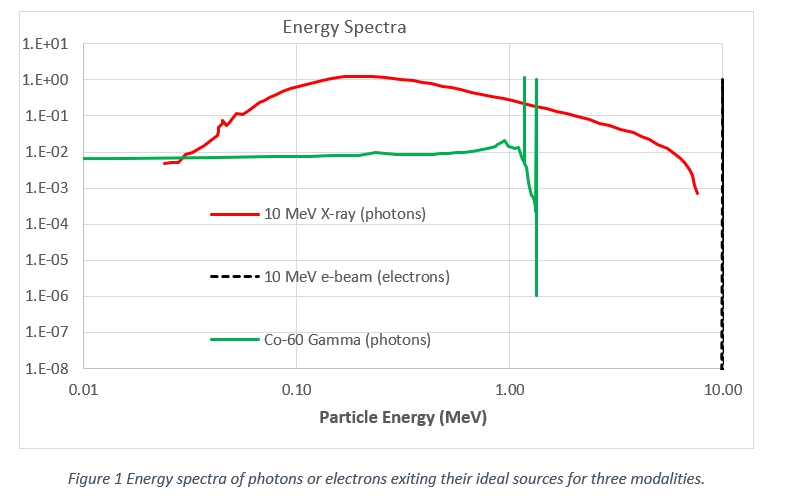
The initial energy spectra of e-beam, x-ray, and gamma sources (Figure 1) for radiation sterilization suggest great dissimilarity in their interaction with materials to be sterilized. However, the energy of ionization events that produce dose is orders of magnitude less than the initial energy of the incident radiation. This work will show that the spectra of energies of the photons and, ultimately, the electrons of the three modalities are indistinguishable in the energy range of importance.
Body
Monte Carlo simulations using MCNP[1] were conducted to simulate the interaction of 10 MeV electrons, 7.5 MeV X-rays, and gamma rays from Cobalt-60 onto totes filled with a polyethylene/air mixture. The spectra of the photons and electrons from all interaction processes were plotted and analyzed for each modality.
Conclusion
Dose is a measure of ionization. Therefore, it is primarily the electrons below 500 keV (the average energy of a Compton electron) that determine the dose delivered to a material. The lack of any significant difference in the spectra of the electrons below 500 keV between these modalities indicates that there should be no difference in their dose deposition due to energy.
References
[1] C.J. Werner(editor), "MCNP Users Manual - Code Version 6.2", Los Alamos National Laboratory, report LA-UR-17-29981 (2017).
This work was produced by Fermi Research Alliance, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC02-07CH11359 with the U.S. Department of Energy. Publisher acknowledges the U.S. Government license to provide public access under the DOE Public Access Plan DOE Public Access Plan.
Lectures by Thomas Kroc
| When | Session | Talk Title | Room |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Wed-09 13:30 - 17:00 |
Posters - Networking - Exhibition | Monte Carlo investigation of the equivalency of the electron and photon spectra of e-beam, x-ray, and gamma radiation | |
|
Tue-08 15:30 - 17:00 |
Tech-4: Progress in EB–X technology | Progress in high-power linacs | Lunar |